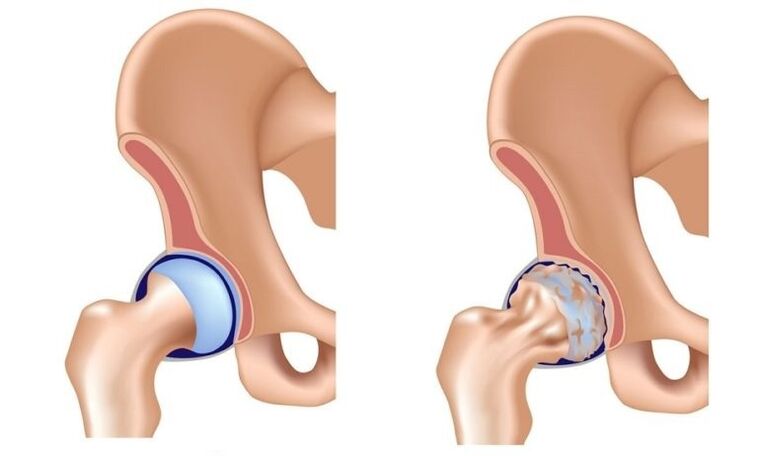
Hook joint arthrosis (deformation of arthrosis, koksarttrosis) is slowly progressive degenerative-dystrophy disease, which is over time that has led to destroy the affected joint, persistent pain and limit mobility.
The disease affects people aged 40, women get sick several times more often than men.
In the overall structure of arthrosis, the hip joint arthrosis belongs to the leading role.This is due to the widespread congenital innate pathology of hip compounds (dysplasia), as well as significant physical effort, which are sensitive.
Risk factors and causes Arthrosis Hook joint
In the pathological development mechanism of the hip joint, the main role belongs to the change in the physicochemical characteristics of the sinovia (inner articular) fluid, as a result of becoming thicker and more visual.It worsens her lubricants.When moving, the wrists of cartilage start rubbed against each other, become rough, covered with cracks.Small particles Hyalin cartilage are abandoned and belonged to the articulated cavity, causing the development of aseptic (nonfective) inflammation in it.As the disease advances into the inflammatory process, bone tissue is drawn into an inflammatory process, which leads to the aseptic necrosis of the breeding head and the surface of acetabulum, creating inflammation and cause strong pain during the movement.
In late measures, the hip joint arthrosis, inflammation was thrown into the surrounding wrist of tissues (blood vessels, nerves, ligaments, muscles), which leads to periarthritis.As a result, the hip joint is completely destroyed, its functions are lost, movement in it ceases.This condition is called ankylosis.
Causes Arthrosis Hook Joint:
- Congenital lip of thigh;
- Hip dysplasia;
- Aseptic Necrosis of femur;
- Peters disease;
- Hook joint injuries;
- Earning arthritis hip joint;
- gonartrosis (deforming osteoarthrosis of a common knee);
- osteochondrosis;
- Excess weight;
- Professional sports;
- Flat feet;
- spine curvature;
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits the characteristics of the structure of the muscle-bone system from parents, which can cause the hip joint arthrosis in these terms.This explains the fact of the existence of families, which is the frequency higher than in the general population.
Forms of disease
Depending on the etiology, the hip joint arthrosis is divided into basic and secondary.Secondary arthrosis develops against the background of other hip joints or his injuries.The primary form is not associated with the previous pathology, the reason for its development is often not possible, in this case they talk about idiopathic arthritis.
Coxartrosis is one- or bilateral.
Phase
Three phases (degrees) differ during the hip joint arthrosis:
- Initial - pathological changes are slightly expressed, provided that timely and adequate treatment is reversible.
- Progressive coexartity - characterized by gradual increase in symptoms (joint pain and damaged mobility), changes in common tissues are already irreversible, but therapy can slow down degenerative processes.
- The final - the movement in the joint is lost, ankylosis is formed.Treatment is possible only surgical (replacement of the compound with artificial).
EndoProsthetics operations in 95% of cases ensure the full reconstruction of the limb mobility, return the patient's performance.
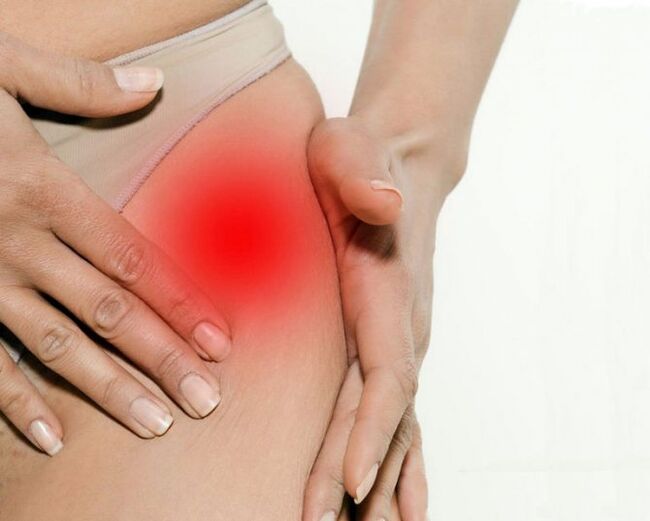
Symptoms of Arthrosis Hook's wrist
Main signs of the Arthrosis Hip joint:
- Pain in groin, hips and knees;
- a feeling of stiffness in the affected joint and the limit of his mobility;
- chromost;
- Abduction limit;
- Atrophic changes in thigh muscles.
The presence of certain symptoms of the hip joint arthrosis, as well as their seriousness depend on the degree of illness.
In the first degree, the patients complain about the pain in the joint joints of the hip joints that occur under the influence of physical activity (extended walking, running).In some cases, the pain is localized in the area of the knee or thigh.After a short break, the pain passes alone.The amount of limbs movement is fully preserved, walking is not broken.The following changes were observed on the radiograph:
- A slight uneven reduction in the lumens of the shared gap;
- Osteofites located on the internal edge of the turn.
All changes from the head of the neck and femora are not revealed.
With II degree Arthrosis hip joints, pain appears and at rest, including at night.After physical activity, the patient begins to schedule, a characteristic "duck" walk was formed.They appear so - a calmer initial pain - after a long period of real estate, the first few steps causes pain and discomfort and then pass, then return after long loads.In the affected joint, the volume of movement (abduction, internal rotation) is limited.The radiograph shows that the common gap is uneven narrow and its lumens is 50% of the norm.Osteofiti are located on the inside and external edge of the common cavity, crossing the boundaries of cartilage.The contours of thigh heads become uneven due to deformation.
With III degree arthrosis of painkillers, intense and constant, without stopping at night.Walking is significantly difficult, the patient is forced to rely on the reed.The volume of the movement in the affected joint is sharply restricted, later completely stopped.Due to the atrophy of the cuckoo muscles, the bowl deviates in the frontal plane, and the limb was shortened.Attempt to compensate for this shortening, patients when walking are forced to refuse the body towards the lesion, which further increases the load to a painful connection.On the radiographs, multiple bone growth were discovered, a significant narrowing of the common gap and the impugned increase in the femur of the femur.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of the hip joint arthrosis is based on the data of the clinical picture of the disease, the results of medical examinations and instrumental studies, including the main value of visualization - radiographs, calculated or magnetic resonant recording.They do not allow not only to determine the presence of hip joints and assess her degree, but also to identify the possible causes of the disease (trauma, youthful epiphysiolysis, Peters' disease).
Differential diagnosis of the hip joint arthrosis with other diseases of the musculoskelo system is quite complicated.In II and III degree Arthrosis hip joint, muscle atrophy develops, which can cause intensive knee joints to drive or gonart (disease of the knee joint).For differential diagnosis of these countries, the palpation of the knees and the hook is palpated, the amount of movement in them is determined, and worked radically.
In the diseases of the spine, in some cases, the nerve roots of the spinal cord with the development of pain syndrome are clenched.Pain can radiate in the hip joint area and mimic the clinical picture of your defeat.However, the nature of the radical syndrome pain is a little different from the Arthrosis Hip joint:
- pain occurs as a result of raising weight or a sharp clumsy movement, not under the influence of physical effort;
- The pain is localized in gluteal, not in the non-governmental end.
With radical syndrome, the patient can take a peaceful leg to the side, while the arthrosis of the hip joint, the abduction is limited.The characteristic sign of radicular syndrome is a positive symptom of tension - the appearance of sharp pain when trying to raise the flat leg on the patient's back.
The hip joint arthrosis affects people over 40 years old, women get sick several times more often than men.
A hook joint arthrosis should also be distinguished by loyal load (trochanthitis).Pable Bursitis develops faster, within a few weeks.He usually precedes significant physical effort or injury.In this disease pain is much more pronounced than the Arthrosis of the hip joint.At the same time, shortening of limbs and limiting its mobility is not detected.
The clinical picture of atypical reactive arthritis and spondylitis surveys can remind the clinical manifestations of the hip joint arthrosis.However, pain occurs in patients generally at night or at rest, when walking does not increase, but, on the contrary, weak.In the morning, patients record stiffness in the joints, which pass after a few hours.
Treatment Arthrosis Hook Hook
Orthopecies deal with treatment Arthrosis hip joints.Conservative therapy is indicated with I and II level of disease.Patients are prescribed by non-anti-inflammatory drugs in a short course.They do not need to be accepted for a long time, because they cannot only be able to negatively influence on the bodies of the gastrointestinal tract, but in combating the regenerative abilities of the hyalin cartilage.
In the treatment mode, the hip joint arthrosa include hydroprosvers and vasodilators, which creates optimal capabilities for recovery of cartilage tissues.With expressed muscular shrubs, it may require the appointment of the central muscle relaxant.
In these cases where it is not possible to stop the pain syndrome with non-steroid anti -infalmal drugs, resort to intra-straight-out injectments of corticosteroids.
Local treatment of the hip joints using heating fats allows you to reduce muscle spasm and a little weakening hurts due to interference.
In compound therapy, the hip joint arthrosis, physiotherapy methods are also used:
- Magnetotherapy;
- inductermia;
- UHF;
- Laser therapy;
- Ultrasonic treatment;
- massage;
- Medical gymnastics;
- Hand therapy.
Food nutrition for the hip joint arthrosis is focused on correcting body weight and normalization of metabolic processes.Reducing body weight reduces the load on the hip joints and thus slows the progression of the disease.
To unload the affected joint, the doctor can recommend that patients go into crutches or cane.
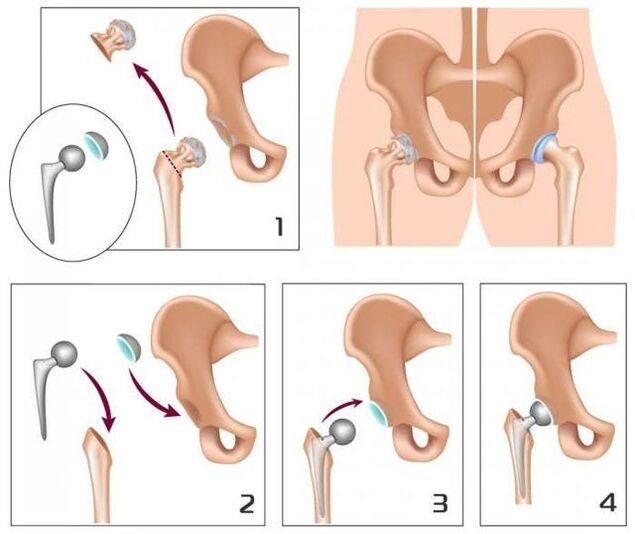
With III degree Arthrosis hip joint, conservative treatment is inefficient.In this case, it is possible to improve the patient's condition, it is possible to restore normal mobility only as a result of surgical intervention - replacing the destroyed compound with artificial (joint endoprosthetics).
Possible consequences and complications
The most serious complication of the progressive arthrosis of the hip joint is a disability due to the loss of the movement in the wrist.In addition to bilateral coxartrosis, the patient loses the ability to transfer the ability and constantly external care is needed.Long stay in bed in one position creates prerequisites for the appearance of stagnant (hyphest) pneumonia, which is difficult to undergo and can lead to death.
Pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits the features of the structure of the muscle-bone system from parents, which can cause the hip joint arthrosis.
Forecast
Arthrosis of hip joints is a progressive chronic disease that can be completely cured only in the early stages, subject to removal of the cause of the disease.In other cases, therapy allows you to slow down your course, however, over time, there is a need for hip endoprosth implantation.Such operations in 95% of cases provide complete reconstruction of limb mobility, return the patient's performance.The life of modern dentures is 15-20 years, after which they are subject to replacement.
Prevention
Prevention of hook joint arthroses aims to remove the causes that can lead to the development of this disease and includes:
- Timely detection and treatment of disease and injuries of hip joint;
- rejection of a sitting lifestyle, regular, but not excessive physical activity;
- body weight control;
- Rational nutrition;
- Refusing bad habits.